Corporate culture
Driver for sustainable corporate success
The success or failure of companies is often attributed to their products and services. However, if we take a closer look, the real reasons for success or failure are probably to be found in the corporate culture.
However, corporate culture is a tricky thing. Everyone knows and feels it, but everyone perceives it very differently. Depending on their position and role, as well as in the context of their personal values and expectations.
However. No other element of organizational theory has such a lasting impact on corporate success in the long term.
But how do you manage and develop an organizational element that is so central on the one hand, but hardly tangible resp. measurable on the other?
The answer to this question is linked to three specific challenges of corporate culture.
The challenges
1. complexity & dynamics
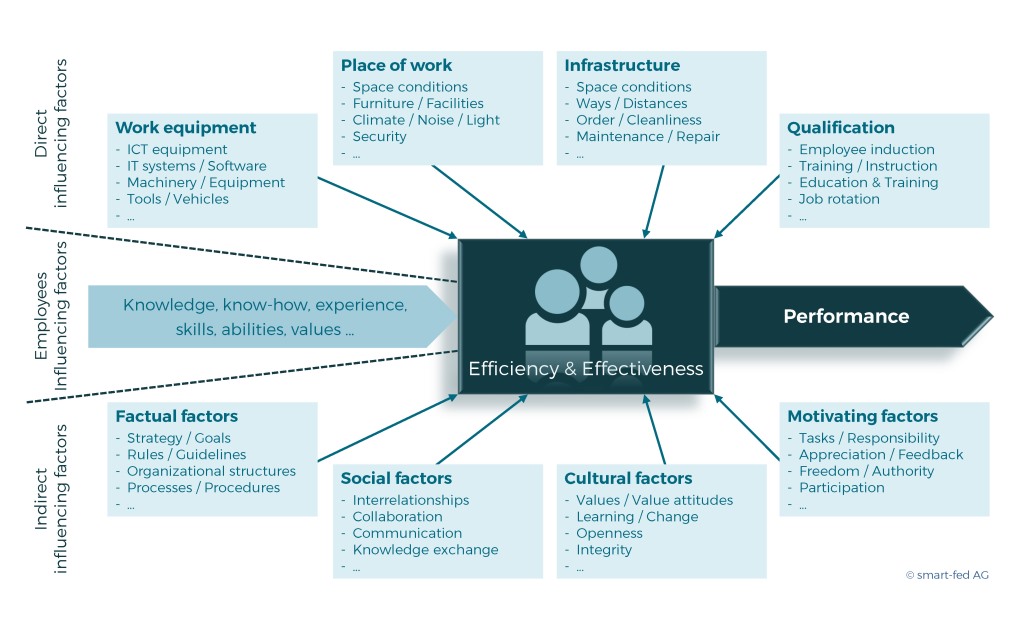
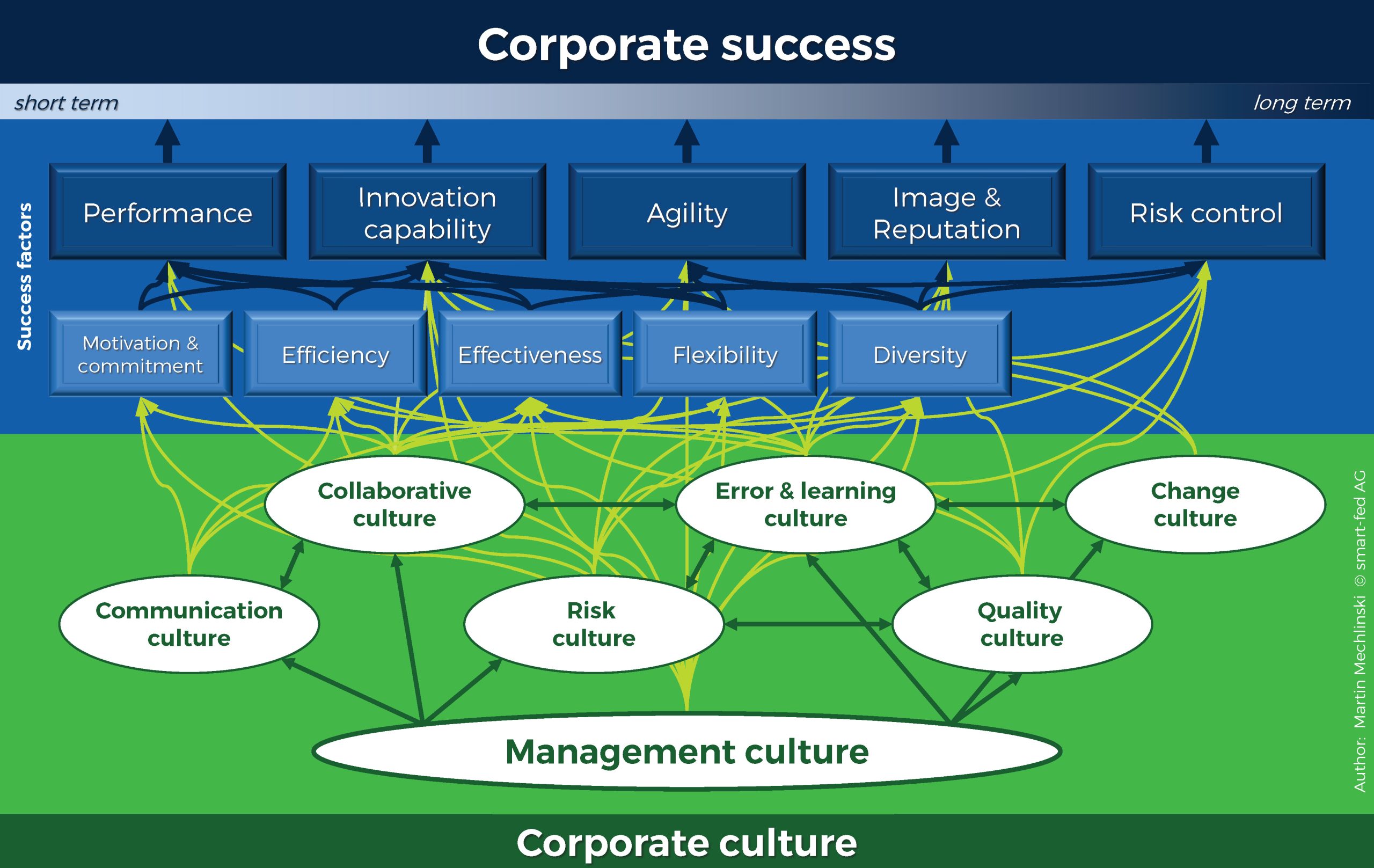
The corporate culture is made up of a large number of subcultures that merge into an overall culture due to their mutual influence and interconnectedness (see graphic).
It is a complex and dynamic combination of different cultural elements with different characteristics and intensity of effect on the central success factors of the company.
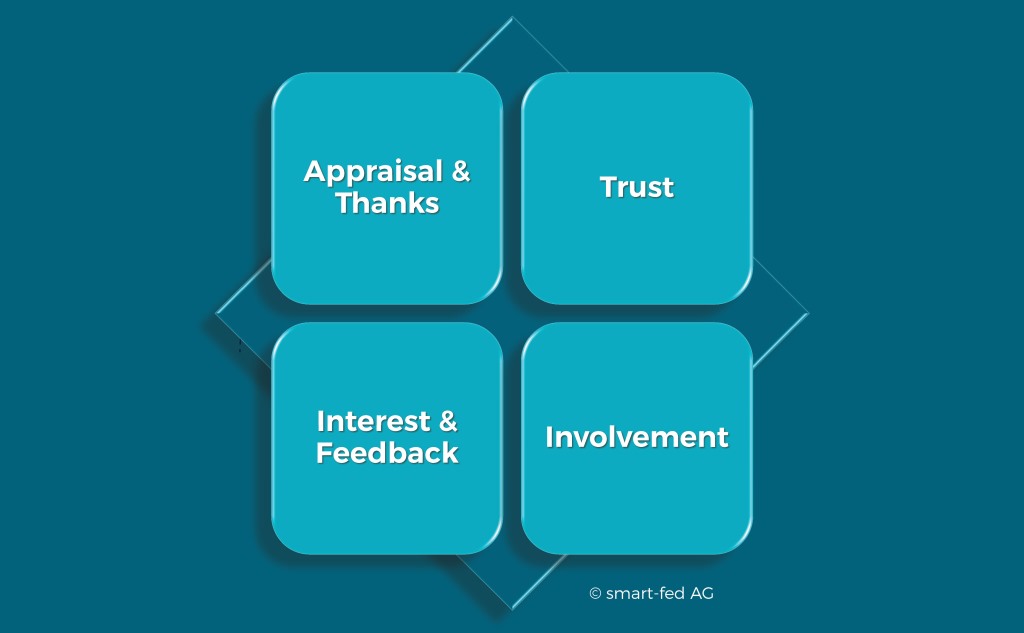
In addition, positive and negative developments cancel each other out or, if they have the same sign, build up. Negative developments in the management culture are particularly critical. As the main driver, it influences all other cultural elements and thus quickly triggers further developments.
2. hidden developments
In order to recognize developments and changes in individual cultural elements in a timely manner and to assess them correctly, sensitive instruments are needed.
This is because cultural changes start locally and initially develop insidiously and hidden in the organizational thicket.
Initial observations and indications therefore receive little attention and are readily swept under the rug. At some point, however, the developments build up and there is a major quake that makes it visible that something is no longer right in the organization.
3. macro & micro cultures
Corporate culture is often regarded as the macro culture of the overall organization. However, it would be a mistake to ignore the micro cultures in the micro-organizations (departments, teams, etc.).
There, too, it is important to have cultural developments on the radar at an early stage, which can have a lasting impact on the company’s success at key points.
Making culture visible
A tool that is intended to make cultural developments and changes in companies transparent must meet the following requirements:
a) It must allow for a comprehensive and continuous scan across all elements of culture so as to have no blind spots, both thematically and temporally.
b) It must accumulate observations over longer periods of time in order to make creeping and hidden developments visible.
c) It must go into depth to track cultural changes in micro-organizations as well.
These three requirements form the core of SMART FED. An efficient and effective management tool for the comprehensive among other things, to identify cultural developments and changes in organizations in a comprehensive, timely and targeted manner.
⇒ Author: Martin Mechlinski / SMART FED
Corporate culture
Driver for sustainable corporate success
The success or failure of companies is often attributed to their products and services. However, if we take a closer look, the real reasons for success or failure are probably to be found in the corporate culture.
However, corporate culture is a tricky thing. Everyone knows and feels it, but everyone perceives it very differently. Depending on their position and role, as well as in the context of their personal values and expectations.
However. No other element of organizational theory has such a lasting impact on corporate success in the long term.
But how do you manage and develop an organizational element that is so central on the one hand, but hardly tangible resp. measurable on the other?
The answer to this question is linked to three specific challenges of corporate culture.
The challenges
1. complexity & dynamics
The corporate culture is made up of a large number of subcultures that merge into an overall culture due to their mutual influence and interconnectedness (see graphic).
It is a complex and dynamic combination of different cultural elements with different characteristics and intensity of effect on the central success factors of the company.
In addition, positive and negative developments cancel each other out or, if they have the same sign, build up. Negative developments in the management culture are particularly critical. As the main driver, it influences all other cultural elements and thus quickly triggers further developments.
2. hidden developments
In order to recognize developments and changes in individual cultural elements in a timely manner and to assess them correctly, sensitive instruments are needed.
This is because cultural changes start locally and initially develop insidiously and hidden in the organizational thicket.
Initial observations and indications therefore receive little attention and are readily swept under the rug. At some point, however, the developments build up and there is a major quake that makes it visible that something is no longer right in the organization.
3. macro & micro cultures
Corporate culture is often regarded as the macro culture of the overall organization. However, it would be a mistake to ignore the micro cultures in the micro-organizations (departments, teams, etc.).
There, too, it is important to have cultural developments on the radar at an early stage, which can have a lasting impact on the company’s success at key points.
Making culture visible
A tool that is intended to make cultural developments and changes in companies transparent must meet the following requirements:
a) It must allow for a comprehensive and continuous scan across all elements of culture so as to have no blind spots, both thematically and temporally.
b) It must accumulate observations over longer periods of time in order to make creeping and hidden developments visible.
c) It must go into depth to track cultural changes in micro-organizations as well.
These three requirements form the core of SMART FED. An efficient and effective management tool for the comprehensive among other things, to identify cultural developments and changes in organizations in a comprehensive, timely and targeted manner.
⇒ Author: Martin Mechlinski / SMART FED